Structural Glazing Glass
R & B Glass Industries Provide superior Quality LOW-E Toughened glass for Structural Glazing.
We can supply LOW-E Glass up to 0.02 Emissivity.
Today structural glazing is the ultramodern "clothing" for facades of buildings and structures of various designation. All projects of structural glazing are fabulously amazing, being light and powerful at the same time. The transparency and openness of these buildings to the outer world reflects aspiration of human society to new design.
Structural glazing is a system of bonding glass to a building's structural framing members utilizing a high strength, high performance silicone sealant specifically designed and tested for structural glazing.In structural glazing applications, dynamic wind loads are transferred from the glass, to the perimeter structural support.
Advantages of Structural Glazing:
- Allows for broader architectural design flexibility
- Increases the thermal efficiency of buildings, because the exterior exposure of metal framing is either reduced or eliminated
- Reduces or eliminates water and air infiltration
- Reduces the potential for thermal breakage of glass.
Types of Structural Gazing
There are many types and systems of structural glazing. These systems are characterized with the use of structural silicone joint sealant for structural fixing of glass or other materials to structural units of the building.
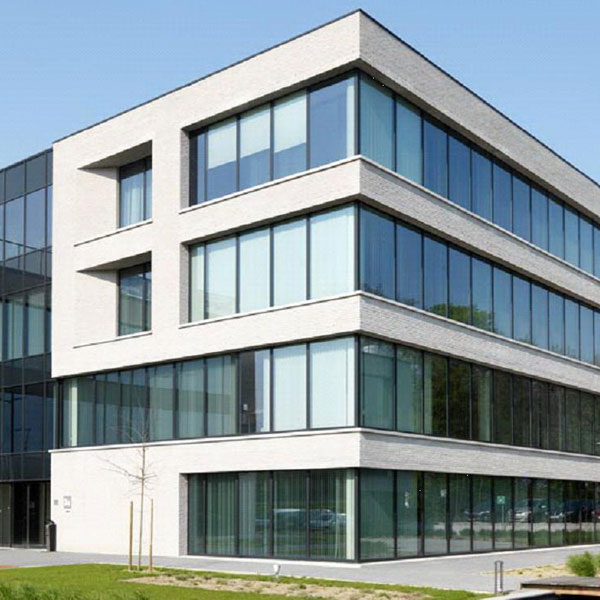
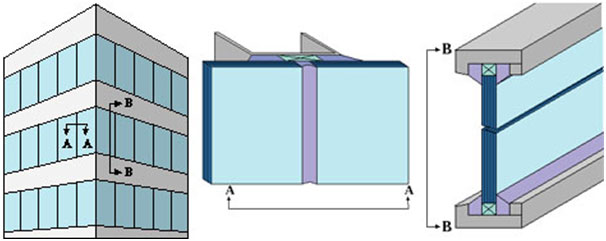
4-sided structural glazing
The most widespread and economic system of structural glazing. Glass is supported from 4 sides by structural silicone. These systems are usually prefabricated and then installed at the construction site.
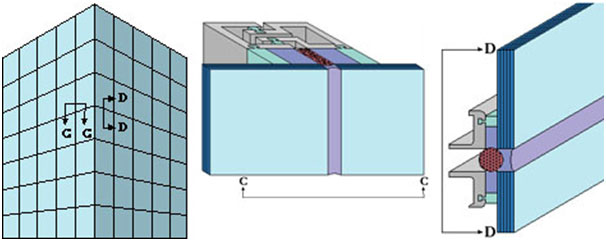
2-Sided Structural Glazing
In these systems silicone is used only on 2 sides of the glass panel. Two other sides of the glass are supported by a mechanical frame or another non-structural method. These systems are prefabricated or assembled at construction site.
Slope Glazing
Slope glazing is glazing applied on other than vertical facades (for example, glazed roofs). In this case, weight of the glass is of major importance. According to European standards, these systems can only use only splinter proof laminated glass. The use of glazing with a negative downgrade is also possible.
Tooth-shape Glazing
In these systems glass units are produced stage by stage: first the exterior panel, then internal panel. Structural joint is mounted on the inside surface of the interior panel of the glass unit.
Systems With U-shaped Profile
In standard systems glass units are fastened to the building by a U-shaped profile. Depending on system design, silicone joint sealant can serve as gasket or structural joint sealant.
Systems With Panoramic Review
These systems are usually mounted on the facade in order to expand the view panorama. Glass ridges are used for structural support of the viewing glass. Silicone is used in the jointing area between glass panel and ridges.
Other Glazing Systems
In these systems silicon joint sealants play an important role in the protection of joints exposed to atmospheric effects, as well against moisture penetration and for insulation of glass panels.
Frameless Glazing Systems
These systems are frequently referred to as "spider systems" or bolted systems. They are not systems of structural glazing in spite of having similar looks. In some designs spider fixtures are only fastening the interior panels of the glass unit. In such designs the joint sealant has a structural function.
Structural Bracing of Non-glass Materials
Structural silicone joint sealant can be used not only for fastening glass materials. It can also be applied for fixing aluminium composites, metal panels, thin epoxy sealed panels of pebble gravel.
Shock Resistant Glazing
Structural silicone joint sealant strongly fixes the laminose glass in the frame during adverse environment conditions (explosion, storm, earthquake, natural cataclysms).



